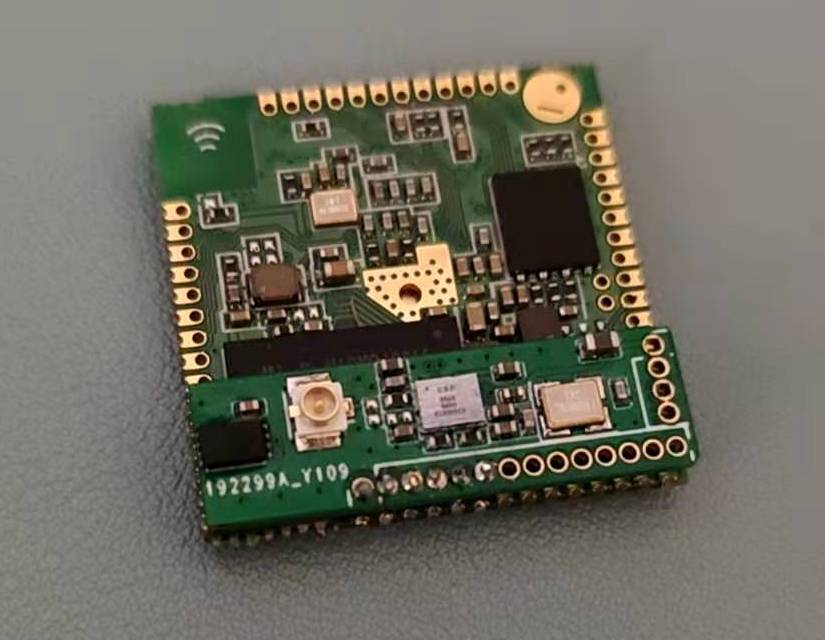
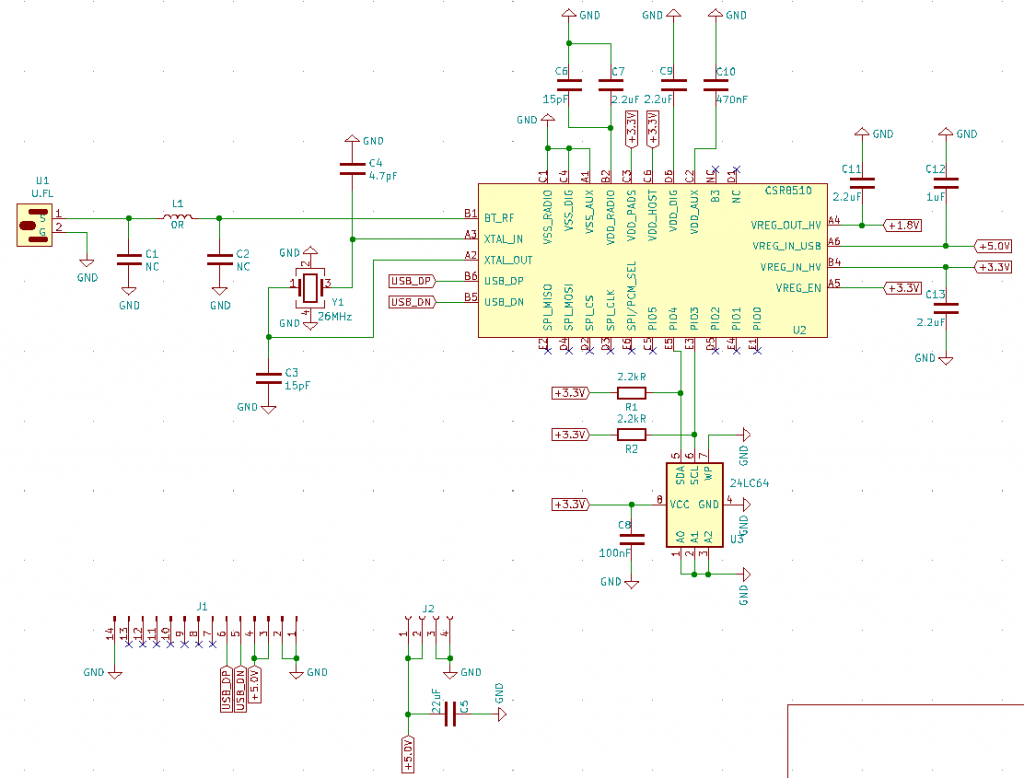
Default VoCore2 only has one ethernet enabled, it is ethernet port0. But actually VoCore2 has 5 ethernet ports. This blog is talking about how to enable them.
First, let’s check the hardware connection.
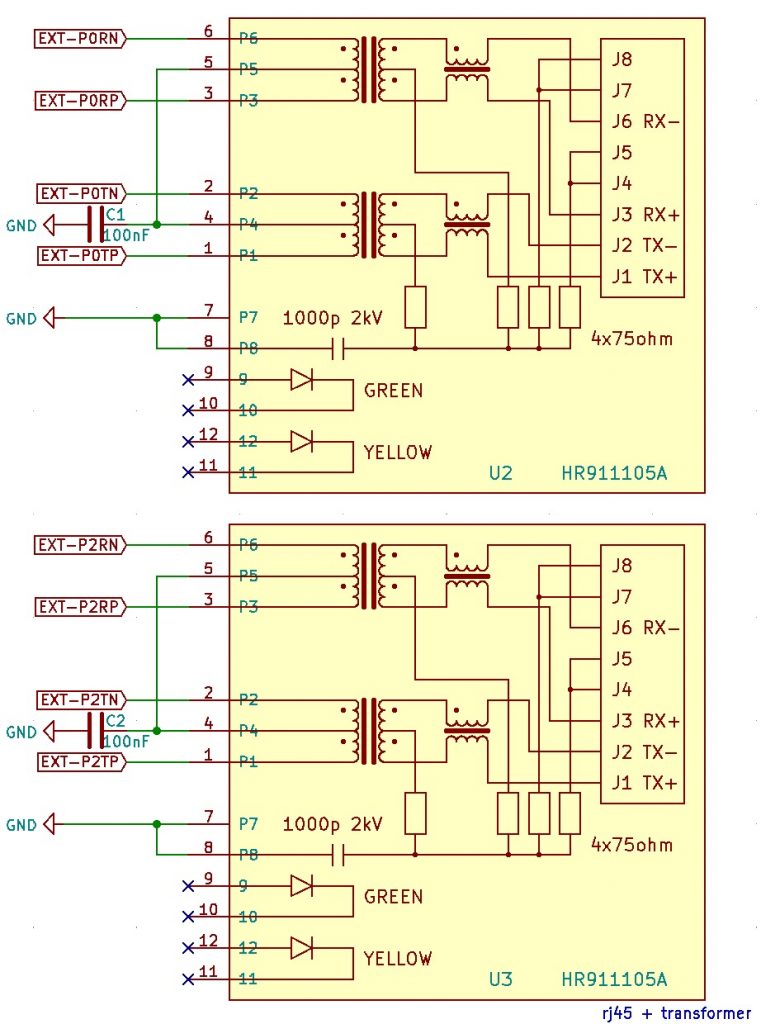
One RJ45 with transformer and one 100nF are enough to make one ethernet port work.
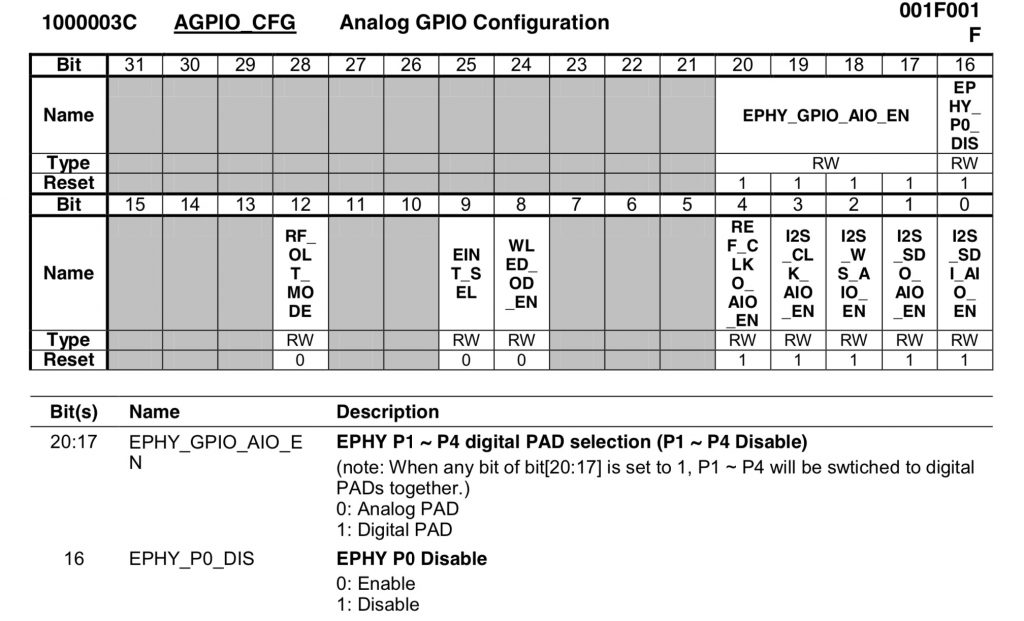
Second, we need to enable ports in kernel level.
This is controlled by register 0x1000003c. In client mode, we can simply use “mem 0x1000003c 0xe001ff” to setup it, or you can use hard way to enable this by device tree.
Once you finish second step, when you plug in or plug out the ethernet cable, you will find a kernel log like “rt3050-esw 10110000.esw: link changed 0x00”;
Port0 plug in: “rt3050-esw 10110000.esw: link changed 0x01”;
Both Port0 and Port2 plug in: “rt3050-esw 10110000.esw: link changed 0x05”
PS: once you enable more than one ethernet, debug port UART2 will be disabled, you will need to change it to UART0/UART1 in VOCORE2.dtsi/VOCORE2.dts; also SDMMC port for SD card is disabled either, please check blog http://vonger.cn/?p=14701 and http://vonger.cn/?p=14435 for tutorial about using 5 ethernet ports and SD card same time.
Third, we need to setup in OpenWrt to enable them
I am not very good at this part, looks like default OpenWrt setting is enabled that two ports, Port0 and Port2, but actually we only have one ethernet by default hardware(VoCore2 Ultimate). So if you only need to use two ports and the ports happens to be Port0 and Port2, you do not need change anything.
If you need to use other ethernet port like ethernet port1, port3, port4, you will need to setup /etc/config/network. Maybe also need to enable them in device tree. This part I am still learning, now I am trying different connection to understand virtual lan, later I will write another blog talk about my learning process. Any suggestions are warm welcome, please email to me(a)vonger.cn or support(a)vocore.io.